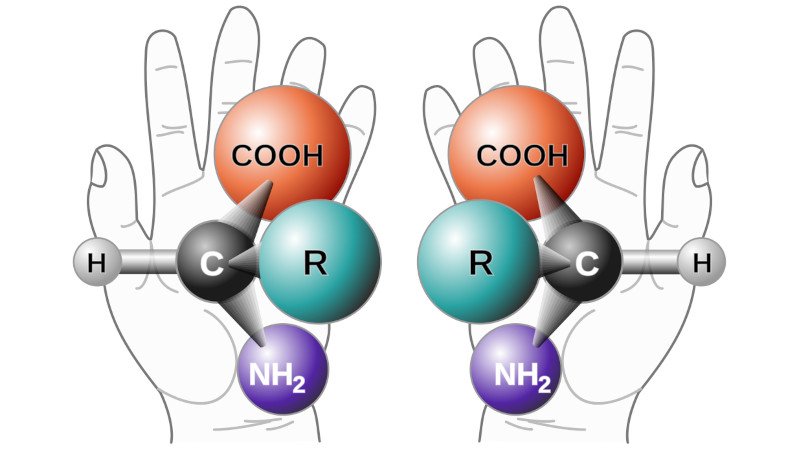
In our high school chemistry classes we all learn about chirality, the property of organic molecules in which two chemically identical molecules can have different structures that are mirror images of each other. This can lead to their exhibiting different properties, and one aspect of chirality is causing significant concerns in the field of synthetic biology. The prospect of so-called mirror organisms is leading to calls from a group of prominent scientists for research in the field to be curtailed due to the risks they would present.
Chirality is baked into all life; our DNA is formed of right-handed molecules while our proteins are left handed. The “mirror” organisms would reverse either or both of these, and could in theory be used to improve biochemical production processes. The concern is that these organisms would evade both the immune systems of all natural life forms, and any human defences such as antibiotics, thus posing an existential risk to life. It’s estimated that the capacity to produce such a life form lies more than a decade away, and the scientists wish to forestall that by starting the conversation early. They are calling for a halt to research likely to result in these organisms, and a commitment from funding bodies not to support such research.
Warnings of the dangers from scientific advances are as old as science itself, and it’s safe to say that many such prophecies have come from dubious sources and proved not to have a basis in fact. But this one, given the body of opinion behind it, is perhaps one that should be heeded.
Header: Original: Unknown Vector: — πϵρήλιο, Public domain.
This articles is written by : Fady Askharoun Samy Askharoun
All Rights Reserved to Amznusa www.amznusa.com
Why Amznusa?
AMZNUSA is a dynamic website that focuses on three primary categories: Technology, e-commerce and cryptocurrency news. It provides users with the latest updates and insights into online retail trends and the rapidly evolving world of digital currencies, helping visitors stay informed about both markets.